VContainer
VContainerは Unity(ゲームエンジン)上で動作する高速なDIフレームワークです。(DI = Dependency Injection のこと。)
"V" は、Unity の頭文字 "U" を 鉛筆削りで鋭く削ってスリムにした形状をイメージしています。
- 高速なResolve: Zenjectとの比較でおよそ 5-10倍の性能 。
- GCにやさしい: オブジェクト解決時 ゼロアロケーション 。(生成したインスタンス自身を除く)
- コンパクトなサイズ: internal 型や .callvirt 命令とかも少ない。ビルドサイズにやさしい。
- 過不足のない機能: シンプルで透明性のあるAPI。過度に複雑で理解し難い設定を避けます。
- イミュータブルなコンテナ: 一度コンテナをつくったら遅い処理がほとんどない。スレッドセーフ。
主な機能
- コンストラクタ インジェクション / メソッド インジェクション / プロパティ & フィールド インジェクション
- PlayerLoopSystem上への 独自C#型のスケジュール
- 柔軟なスコープ生成
- Roslyn SourceGeneratorによる高速化
- Diagnostics Window
- UniTask連携
- ECS連携 beta
DI + Inversion of Control for Unity
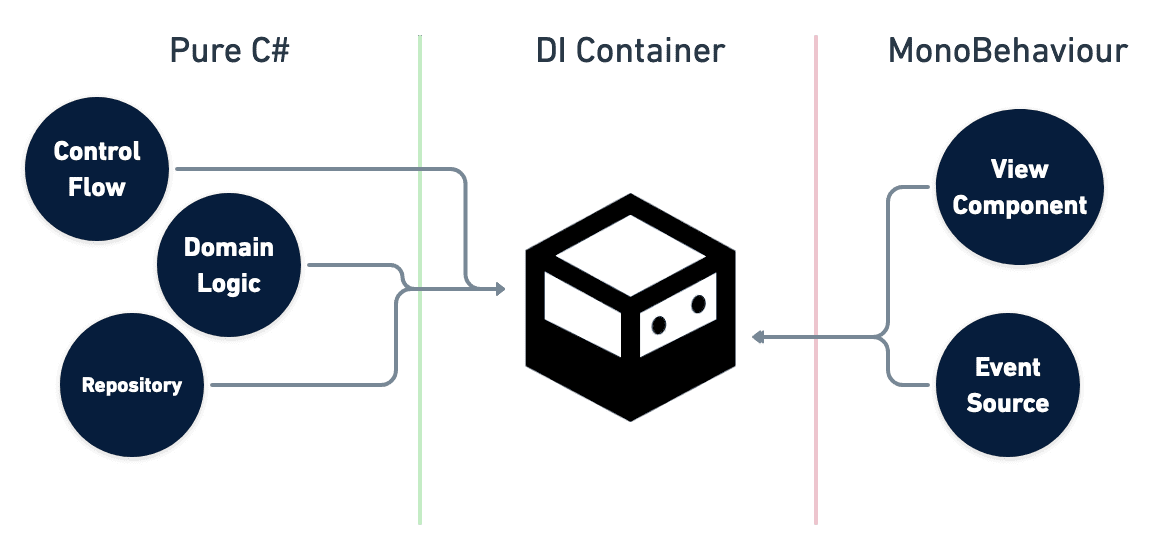
通常、Unityは MonoBehaviour を継承したクラスのみを処理の起点にできますが、VContainerを用いることでオブジェクト同士の参照関係/所有関係を自由に構築したり、純粋なC# クラスのエントリポイントをつくることができます。これはUnityのコンポーネントに依存する部分・見た目の部分と、その他純粋なロジックを分離する設計の手助けになります。
このような制御の反転はIoC(Inversion of Control) などと呼ばれていて、DIコンテナの設計上の利点のひとつです。
- くわしくは:
- 合わせて読みたい:
パフォーマンス
Benchmark result for 10,000 iterations for each test case (Unity 2019.x / IL2CPP Standalone macOS)
- デフォルトでは、VContainerやZenjectはDIのために実行時のリフレクションを使います。
- "VContainer (CodeGen)" は コンパイル時 IL コード生成による高速化モード時の性能です。
GC Alloc result in the Resolve Complex test case (Unity Editor profiled)
基本の使い方
VContainerを使うには、最初にスコープを表現するコンポーネントを作成します。設定をC#コードで記述することで、自動的にオブジェクト同士の参照が組み立てられます。
public class GameLifetimeScope : LifetimeScope
{
public override void Configure(IContainerBuilder builder)
{
builder.RegisterEntryPoint<ActorPresenter>();
builder.Register<CharacterService>(Lifetime.Scoped);
builder.Register<IRouteSearch, AStarRouteSearch>(Lifetime.Singleton);
builder.RegisterComponentInHierarchy<ActorsView>();
}
}
クラス定義の例)
public interface IRouteSearch
{
/* ... */
}
public class AStarRouteSearch : IRouteSearch
{
/* ... */
}
public class CharacterService
{
readonly IRouteSearch routeSearch;
public CharacterService(IRouteSearch routeSearch)
{
this.routeSearch = routeSearch;
}
}
public class ActorsView : MonoBehaviour
{
// ...
}
public class ActorPresenter : IStartable
{
readonly CharacterService service;
readonly ActorsView actorsView;
public ActorPresenter(
CharacterService service,
ActorsView actorsView)
{
this.service = service;
this.actorsView = actorsView;
}
void IStartable.Start()
{
// VContainerのPlayerLoopSystemが`Start`を呼び出します。
}
}
- この例では、
CharacterServiceのrouteSearchが自動的にAStarRouteSearchのインスタンスとして設定されます。 - エントリポイントとして登録した
ActorPresenterは,Unityのライフサイクル上にスケジュールされます。 - くわしくは:
動的なスコープ生成と非同期
LifetimeScopeは、動的に子スコープを作ることができます。ゲームでよく発生する非同期のリソース読み込みに対応できます。
public void LoadLevel()
{
// ... 追加のアセットを実行時に読み込んだりする ...!
// 子スコープ作成の例
instantScope = currentScope.CreateChild();
// 特定のプレハブを使用した子スコープ作成の例
instantScope = currentScope.CreateChildFromPrefab(lifetimeScopePrefab);
// 追加でインスタンスを登録した子スコープ作成の例
instantScope = currentScope.CreateChildFromPrefab(
lifetimeScopePrefab,
builder =>
{
// Extra Registrations ...
});
instantScope = currentScope.CreateChild(builder =>
{
// ExtraRegistrations ...
});
instantScope = currentScope.CreateChild(extraInstaller);
}
public void UnloadLevel()
{
// スコープの破棄
// コンテナが管理しているオブジェクトもDisposeされる
instantScope.Dispose();
}
また、追加のUnityシーンをAdditiveで読み込む際に、LifetimeScopeの親子関係を作ることもできます。
class SceneLoader
{
readonly LifetimeScope currentScope;
public SceneLoader(LifetimeScope currentScope)
{
currentScope = currentScope; // Inject the LifetimeScope to which this class belongs
}
IEnumerator LoadSceneAsync()
{
// LifetimeScope generated in this block will be parented by `this.lifetimeScope`
using (LifetimeScope.EnqueueParent(currentScope))
{
// If this scene has a LifetimeScope, its parent will be `parent`.
var loading = SceneManager.LoadSceneAsync("...", LoadSceneMode.Additive);
while (!loading.isDone)
{
yield return null;
}
}
}
// UniTask example
async UniTask LoadSceneAsync()
{
using (LifetimeScope.EnqueueParent(parent))
{
await SceneManager.LoadSceneAsync("...", LoadSceneMode.Additive);
}
}
}
// LifetimeScopes generated during this block will be additionally Registered.
using (LifetimeScope.Enqueue(builder =>
{
// Register for the next scene not yet loaded
builder.RegisterInstance(extraInstance);
}))
{
// Loading the scene..
}
- くわしくは:
UniTask
async UniTask なメソッドを処理の起点にすることもできるようになっています。
public class FooController : IAsyncStartable
{
public async UniTask StartAsync(CancellationToken cancellation)
{
await LoadSomethingAsync(cancellation);
await ...
...
}
}
builder.RegisterEntryPoint<FooController>();
- くわしくは:
Diagnostics
Unityエディタ上で動作するデバッグツールが同梱されています。